We all know how convenient it is to use SQL variables in queries and stored procedures, but there are big differences in the SQL statement syntax and use of variables for Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle and PostgreSQL which we will cover in this tutorial.
In this tutorial we will review the different ways to declare and use variables and placeholders in SQL Server, Oracle and PostgreSQL. We will also see the various differences in syntax and logic as well as types of variables for various SQL databases.
As always, we will use the github freely downloadable database sample Chinook, as it is available in multiple RDBMS formats. It is a simulation of a digital media store, with some sample data, all you have to do is download the version you need and you have all the scripts for data structure and all the inserts for data.
In SQL Server we can define variables, also known as local variables, both in ad hoc queries and in Stored Procedures with T-SQL logic. The process is quite straightforward using the DECLARE clause in both cases and the variables are identified by a preceding "@" plus the variable name.
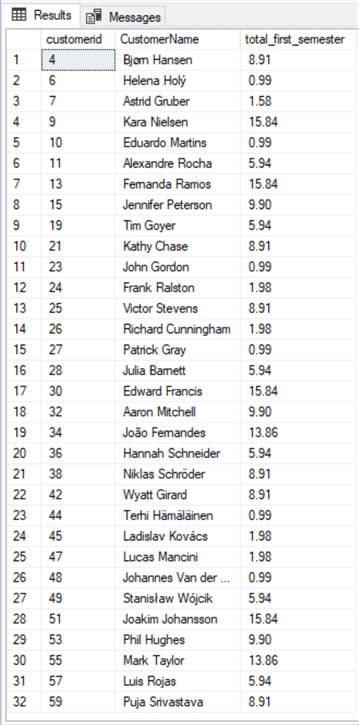
Let's look at a quick SELECT statement in the following example using variables in a query where we need to calculate the total purchased by customer for the first half of 2012.
declare @date_start as date = '01/01/2012' -- value of the variable declare @date_end as date = '07/01/2012' -- value of the variable select invoice.customerid, firstname + ' ' + lastname as CustomerName, sum(total) as total_first_semester from Invoice inner join Customer on invoice.CustomerId = Customer.CustomerId where InvoiceDate >= @date_start and InvoiceDate < @date_end group by invoice.customerid, firstname + ' ' + lastname

AsAs you can see, there are two declare statements for the two variables with DATE data type and assigned values to them. I then used those variables in the WHERE clause instead of typing the dates. The obvious advantage of doing that is that if we're going to use those dates in more than one place or change them, we just need to modify the value assigned to the local variable. Quite easy!
In Oracle is possible to define variables in queries, procedures and packages with some differences between the way in which it can be done.
First of all, we can have binding variables that are identified by a preceding ":".
In an ad hoc query they are used more as placeholders, and we do not need to use the DECLARE clause like in SQL Server.
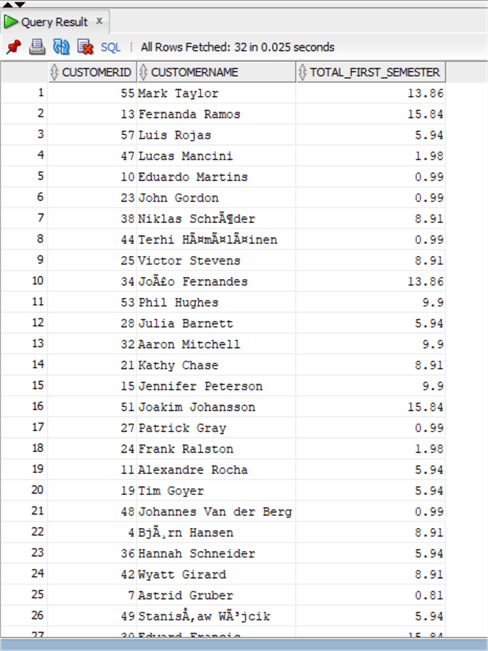
SELECT chinook.invoice.customerid, firstname || ' ' || lastname as CustomerName, sum(total) as total_first_semester from chinook.Invoice inner join chinook.Customer on invoice.CustomerId = Customer.CustomerId where InvoiceDate >= to_date(:Date_Start,'mm/dd/yyyy') and InvoiceDate < to_date(:Date_End,'mm/dd/yyyy') group by invoice.customerid, firstname || ' ' || lastname;
As you can see I have inserted the :Start_date and :End_date as binding variables in the WHERE clause of the query (with a formatting for date) and when I run it I am prompted to insert the values.
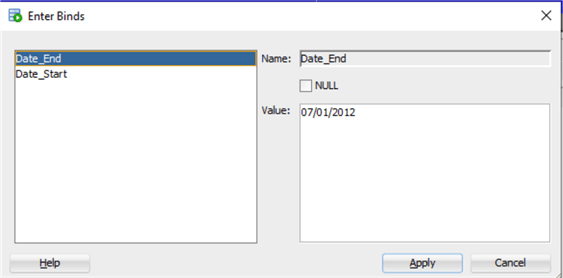
There is also another syntax supported by queries that is much more similar to SQL Server.
DEFINE Date_Start = TO_DATE('01/01/2012','mm/dd/yyyy'); DEFINE Date_End = TO_DATE('07/01/2012', 'mm/dd/yyyy'); SELECT chinook.invoice.customerid, firstname || ' ' || lastname as CustomerName, sum(total) as total_first_semester from chinook.Invoice inner join chinook.Customer on invoice.CustomerId = Customer.CustomerId where InvoiceDate >= &Date_Start and InvoiceDate < &Date_End group by invoice.customerid, firstname || ' ' || lastname;
In this case I declare the variables with the DEFINE clause and assign them a value on the same line just like in SQL Server, then I used them in the WHERE clause, this time preceding them with an "&". Notice that in the declaration phase the "&" is not needed.
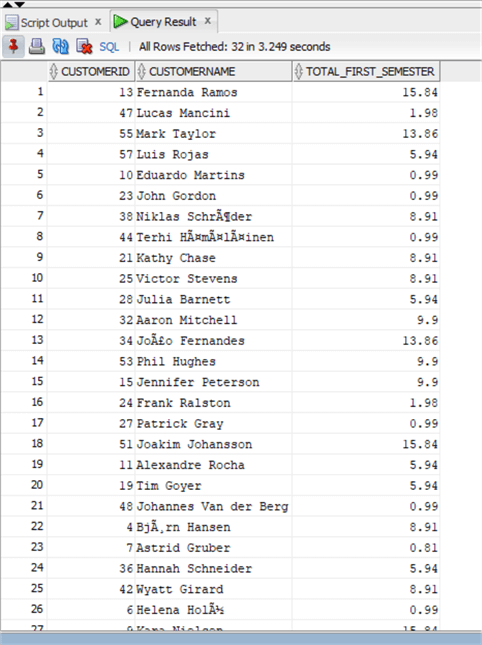
Both syntaxes and ways are supported in queries without the need of a PL/SQL block. In fact inside a PL/SQL block it is not possible to use a variable in order to filter data as we have just done above, because inside a block it is expected that the query assigns values to the variables with a SELECT .. INTO type of query, let's do an example extracting a specific customer First and Last name and return it using the DBMS_OUTPUT clause as I did in this tip: INSERT INTO for SQL Server, Oracle and PostgreSQL returning the value assigned to a variable.
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON DECLARE First_name VARCHAR2(40); Last_name VARCHAR2(20); BEGIN select firstname, lastname into First_name, Last_name from chinook.customer where customerid=10; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(First_name || ' ' || Last_name); END;
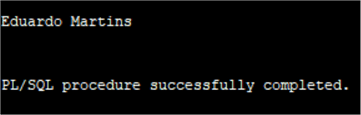
It is also possible to declare the variables as the same data type as a column in a table, in this way the variables are "anchored" to the column data type: if it changes the variable will also change.
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON DECLARE First_name chinook.customer.firstname%TYPE; Last_name chinook.customer.lastname%TYPE; BEGIN select firstname, lastname into First_name, Last_name from chinook.customer where customerid=10; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(First_name || ' ' || Last_name); END;
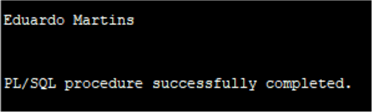
In PostgreSQL there is not the possibility to use variables in an ad hoc query (unless using or more properly abusing CTEs) but only in PL/pgSQL blocks, such as functions/procedures, but also as in line code blocks. As in the other RDBMS this is done with the clause DECLARE. Let's do the same example.
DO $$ DECLARE date_start DATE := '2012-01-01'; date_end DATE := '2012-07-01'; BEGIN create temp table temp_table (CustomerId integer, CustomerName character varying(61), total_first_semester numeric(10,2)); insert into temp_table SELECT "Invoice"."CustomerId", "FirstName"||' '||"LastName" as "CustomerName", sum("Total") as total_first_semester from "Invoice" inner join "Customer" on "Invoice"."CustomerId" = "Customer"."CustomerId" where "InvoiceDate" >= date_start and "InvoiceDate" < date_end group by "Invoice"."CustomerId", "FirstName" || ' ' || "LastName"; END $$; select * from temp_table
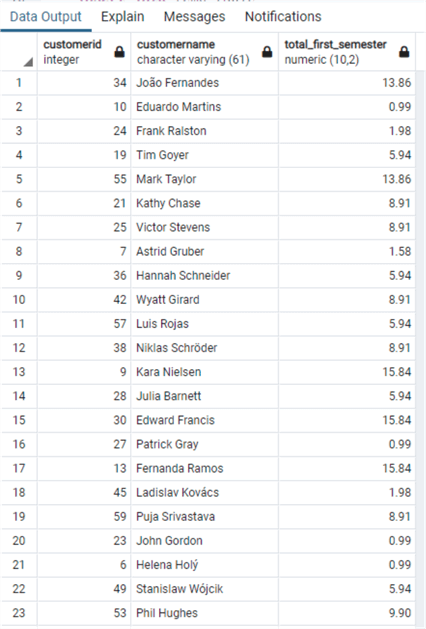
Here we have a few things to note: first, in order to have an inline code block I had to use the DO $$ and END $$ in order to delimitate the block. Second, I had to assign the rows returned by the query to a temporary table in order to present it, otherwise I would have had an error. Finally, the variables are not identified by special characters, but they can be declared and assigned in the same row as in the other RDBMS.
So far we have seen how to declare and use variables in queries or code blocks similar to ad hoc queries, let's see now how they behave in procedures.
In SQL Server, as I pointed out at the beginning, the variables are treated the same way for ad hoc queries and stored procedures. Let's do a quick and easy example where we need to write a stored procedure returning the First Name and Last Name of a customer given its CustomerId.
SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO -- ============================================= -- Author: Andrea Gnemmi -- Create date: 02/02/2022 -- Description: Returns FirstName LastName of CustomerId -- ============================================= CREATE PROCEDURE Get_Customer @CustomerId int AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON; SELECT FirstName + ' ' + LastName from customer where customerid = @CustomerId END
I created a very simple stored procedure here, using the variable @CustomerId as the input parameter, now we execute it as follows.
EXEC Get_Customer 11 -- variable value
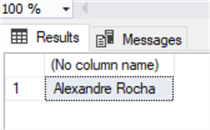
Pay attention though, in this example I have not used a local variable but instead a parameter, so let's imagine that in this stored procedure we need to also check VIP customers which are identified by the SupportRepId being the sales manager. So I modify the stored procedure as follows.
SET ANSI_NULLS ON GO SET QUOTED_IDENTIFIER ON GO -- ============================================= -- Author: Andrea Gnemmi -- Create date: 02/02/2022 -- Description: Returns FirstName LastName of CustomerId -- ============================================= ALTER PROCEDURE [dbo].[Get_Customer] @CustomerId int AS BEGIN SET NOCOUNT ON; DECLARE @RepId as integer; DECLARE @Vip as integer=2; SELECT @RepId = SupportRepId from Customer where customerid = @CustomerId IF @RepId = @Vip BEGIN SELECT 'This is a VIP Customer ' + FirstName + ' ' + LastName from customer where customerid = @CustomerId END ELSE BEGIN SELECT FirstName + ' ' + LastName from customer where customerid = @CustomerId END END
In this case I've declared two local variables: @RepId stores the value of column SupportRepId returned with a query and @Vip stores the EmployeeId of the actual Sales Manager. Let's try it out.
exec Get_Customer 13 -- variable value
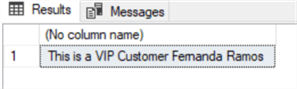
exec Get_Customer 7 -- variable value
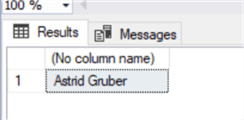
Let's create the same procedure in Oracle, already considering the second one with the internal variables and IF logic.
create or replace PROCEDURE CHINOOK.GET_CUSTOMER (INCUSTOMERID IN NUMBER, RESULTAT OUT VARCHAR2) AS REPID NUMBER; VIP NUMBER:=2; BEGIN SELECT SUPPORTREPID INTO REPID FROM CHINOOK.CUSTOMER WHERE CUSTOMERID = INCUSTOMERID; IF REPID = VIP THEN SELECT 'This is as VIP Customer ' || FIRSTNAME || ' ' || LASTNAME INTO RESULTAT FROM CHINOOK.CUSTOMER WHERE CUSTOMERID = INCUSTOMERID; ELSE SELECT FIRSTNAME || ' ' || LASTNAME INTO RESULTAT FROM CHINOOK.CUSTOMER WHERE CUSTOMERID = INCUSTOMERID; END IF; END;
Please notice that we do not need the DECLARE clause for the variables and the different syntax for the IF THEN ELSE.
In order to return the procedure's output, we have to assign it to a variable and run the same DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE that we've used before.
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON DECLARE INCUSTOMERID NUMBER; RESULTAT VARCHAR2(200); BEGIN INCUSTOMERID := 13; CHINOOK.GET_CUSTOMER( INCUSTOMERID => INCUSTOMERID, RESULTAT => RESULTAT ); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('RESULTAT = ' || RESULTAT); END;
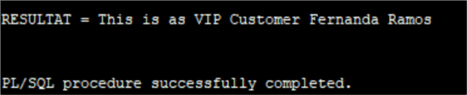
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON DECLARE INCUSTOMERID NUMBER; RESULTAT VARCHAR2(200); BEGIN INCUSTOMERID := 7; CHINOOK.GET_CUSTOMER( INCUSTOMERID => INCUSTOMERID, RESULTAT => RESULTAT ); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('RESULTAT = ' || RESULTAT); END;
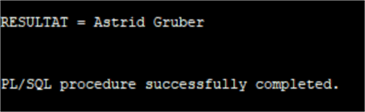
We can do the same in PostgreSQL, but in order to return a value from the procedure we need to use a FUNCTION and the syntax here is slightly different.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION get_customer(IN idcustomer integer) RETURNS table(customername text) AS $$ DECLARE vip integer:=2; repid integer; BEGIN repid:=(select "SupportRepId" from "Customer" where "CustomerId" = idcustomer); IF repid = vip then return query Select 'This is as VIP Customer ' || "FirstName" || ' ' || "LastName" from "Customer" where "CustomerId" = idcustomer; else return query Select "FirstName" || ' ' || "LastName" from "Customer" where "CustomerId" = idcustomer; end if; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
So a few comments on the syntax. In order to return a result set in a PostgreSQL function we need to specify the RETURNS table clause, then we assign the value of the select query directly to the variable repid with a syntax slightly different from both SQL Server and Oracle. Last but not least, we return the result set with the RETURN QUERY clause. Notice that we need to specify the language as PLPGSQL in order to make use of the IF THEN ELSE cycle.
We can then execute the function with a simple SELECT.
select get_customer(13)
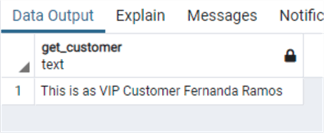
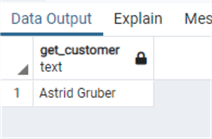
select get_customer(7)
In this tutorial we reviewed various way to declare and use variables in SQL Server, Oracle and PostgreSQL. We also looked at differences in procedure syntax. Stay turned for future tutorials on stored procedures, system variables, dynamic SQL and more.






Andrea Gnemmi is a Database and Data Warehouse professional with almost 20 years of experience, having started his career in Database Administration with SQL Server 2000.
This author pledges the content of this article is based on professional experience and not AI generated.
Article Last Updated: 2022-09-19